Measurement of Di-jet Cross-Sections in Photoproduction and Photon Structure
|
The photon has been shown to often assume the characteristics of a
hadronic fluctuation when interacting with hadronic matter. The hadronic
fluctuation may form a bound meson carrying the quantum number of the photon
or lead to quasi free partons, i.e. quarks and gluons, interacting separately
with the hadronic target. The latter process is commonly described as the
resolved process. In this picture it is meaningful to determine the partonic
content of the photon. This measurement describes the extraction of the
gluonic component of the photon thus complementing measurements at e+e-
colliders which probe its quark content.
To achieve this the H1 experiment has used a sample of photoproduction
events with an explicit di-jet structure. In order to ensure sufficiently
energetic interactions between a quasireal photon and a proton, the electron
was tagged under very small angles and selected to carry roughly half the
energy of the incident lepton beam. At lowest order the two jets originate
from the hard interaction between a parton of the proton and a parton with
momentum fraction xgamma in the photon. Since the partonic content
of the proton has been well measured the partonic content of the photon
can be inferred by an unfolding procedure.
The extraction procedure is severely hampered at small transverse momenta
of the jets by the influence of multiple partonic interactions which are
not easily included in the theoretical description. However, at larger
ET perturbative QCD is able to successfully describe the measured
distributions without being dominated by such disturbing influences. H1
has measured the influence of the underlying events and hence could extract
the gluonic component in the photon (see figure).
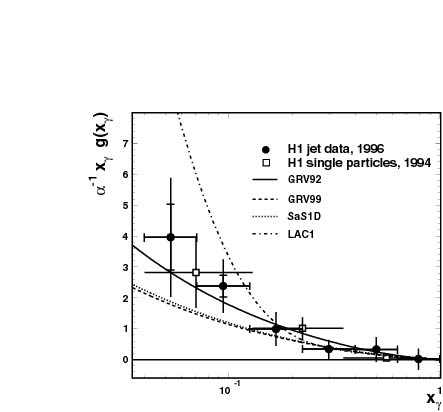 The
number of gluons in the photon is seen to rise with decreasing xgamma,
an observation that has also been made for the gluon component in the proton.
This feature seems to be a general property of quarkonic matter surrounded
by gluons. The measured distribution is well described by a QCD model (in
leading order perturbation theory).
The
number of gluons in the photon is seen to rise with decreasing xgamma,
an observation that has also been made for the gluon component in the proton.
This feature seems to be a general property of quarkonic matter surrounded
by gluons. The measured distribution is well described by a QCD model (in
leading order perturbation theory).
Last Update Feb 29, 2000, E. Elsen
 The
number of gluons in the photon is seen to rise with decreasing xgamma,
an observation that has also been made for the gluon component in the proton.
This feature seems to be a general property of quarkonic matter surrounded
by gluons. The measured distribution is well described by a QCD model (in
leading order perturbation theory).
The
number of gluons in the photon is seen to rise with decreasing xgamma,
an observation that has also been made for the gluon component in the proton.
This feature seems to be a general property of quarkonic matter surrounded
by gluons. The measured distribution is well described by a QCD model (in
leading order perturbation theory).