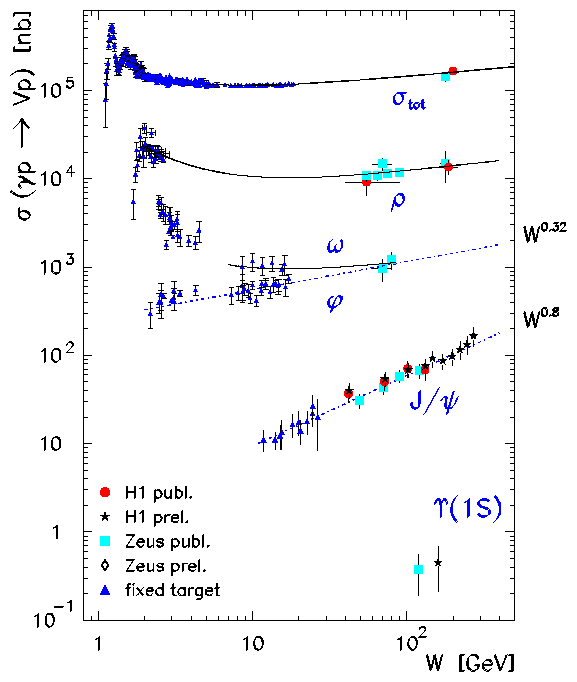
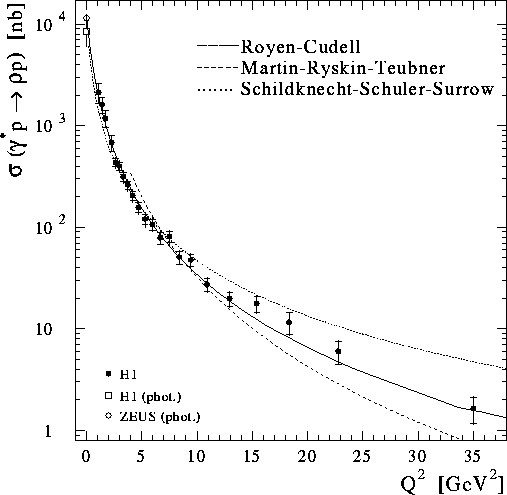
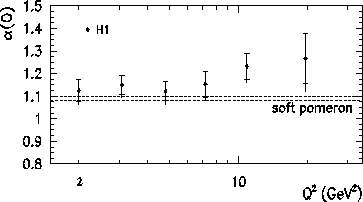
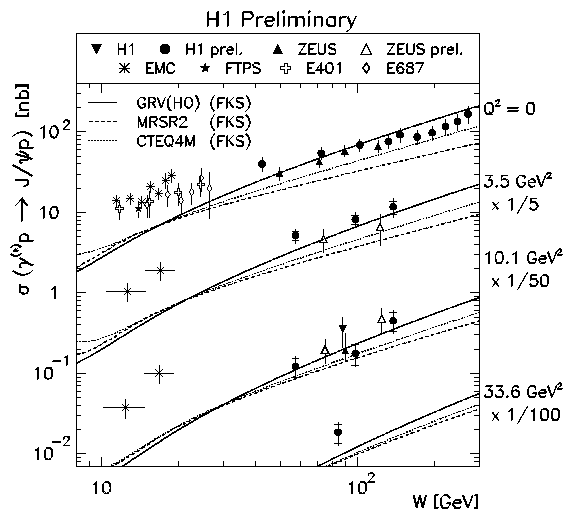
- Elastic vector meson production from ep collisions involve the exchange
of a colour singlet object which is emitted by the proton.
Of special interest are processes with a hard scale such as
the mass MV of a heavy vector meson,
the virtuality Q2 of the photon in a deep inelastic scattering process, or
the squared four-momentum transfer t of the colour singlet exchange.
Such processes allow perturbative QCD calculations to be compared with the measurements and therefore give new information on colour singlet exchange as well as on the proton and the vector meson.